Category: IP routing
… updated on Thursday, June 1, 2023 16:32 UTC
Source IP Address in Multicast Packets
One of my readers sent me this (paraphrased) question:
What I have seen in my network are multicast packets with the IP source address set to 0.0.0.0 and source port set to 0. Is that considered acceptable? Could I use a multicast IP address as a source address?
TL&DR: **** NO!!!
It also seemed like a good question to test ChatGPT, and this time it did a pretty good job.
Why Is Source Address Validation Still a Problem?
I mentioned IP source address validation (SAV) as one of the MANRS-recommended actions in the Internet Routing Security webinar but did not go into any details (as the webinar deals with routing security, not data-plane security)… but I stumbled upon a wonderful companion article published by RIPE Labs: Why Is Source Address Validation Still a Problem?.
The article goes through the basics of SAV, best practices, and (most interesting) using free testing tools to detect non-compliant networks. Definitely worth reading!
DHCP Relaying in EVPN VRFs
After figuring out how DHCP relaying works and testing it with VRFs and in VXLAN segments, it seems like a no-brainer to make it work with EVPN.
TL&DR: It works, at least when using Arista vEOS as the relay and Cisco CSR 1000v as the DHCP server.
Lab Topology
We’ll keep using the exact same “physical” topology we used in the VXLAN DHCP relaying lab, add EVPN and BGP to the control-plane cocktail, and put the VXLAN segment into a VRF. We’ll use CSR 1000v as the DHCP server because Cisco IOSv doesn’t support some of the DHCP option-82 sub-options we need.
DHCP Relaying in VXLAN Segments
After I got the testing infrastructure in place (simple DHCP relay, VRF-aware DHCP relay), I was ready for the real fun: DHCP relaying in VXLAN (and later EVPN) segments.
TL&DR: It works exactly as expected. Even though I had anycast gateway configured on the VLAN, the Arista vEOS switches used their unicast IP addresses in the DHCP relaying process. The DHCP server had absolutely no problem dealing with multiple copies of the same DHCP broadcast relayed by different switches attached to the same VLAN. One could only wish things were always as easy in the networking land.
Test VRF-Aware DHCP Relaying with netlab
After figuring out how DHCP relaying works and testing it in a simple lab, I went a step further and tested VRF-aware DHCP relaying.
Lab Topology
I had to make just a few changes to the DHCP relaying lab topology:
- DHCP server is running on CSR 1000v. IOSv DHCP server does not support subnet selection DHCP option and thus doesn’t work with relays that do inter-VRF DHCP relaying.
- I put the link between the DHCP client and DHCP relay into a VRF.
Test DHCP Relaying with netlab
After figuring out how DHCP relaying works, I decided to test it out in a lab. netlab has no DHCP configuration module (at the moment); the easiest way forward seemed to be custom configuration templates combined with a few extra attributes.
Lab Topology
This is how I set up the lab:
DHCP Relaying Details
Chinar Trivedi asked an interesting question about DHCP relaying in VXLAN/EVPN world on Twitter and my first thought was “that shouldn’t be hard” but when I read the first answer that turned into “wait a minute, how exactly does DHCP relaying works?”
I’m positive there’s a tutorial out there somewhere, but I decided to go back to the sources of wisdom: the RFCs. It turned out to be a long walk down the IETF history lane.
Video: Link State Routing Protocol Basics
The Routing Protocols Overview part of How Networks Really Work webinar introduced the concepts of distance-vector and link-state routing protocols. Next step: the basics of link-state routing protocols.
IRB Models: Edge Routing
The simplest way to implement layer-3 forwarding in a network fabric is to offload it to an external device1, be it a WAN edge router, a firewall, a load balancer, or any other network appliance.
Routing at the (outer) edge of the fabric
Worth Reading: Routing Protocol Implementation Evaluation
In 2018 I tried to figure out whether the rush to deploy new routing protocols in leaf-and-spine fabrics is anything more than another blob of hype (RIFT, OpenFabric, BGP), considering OSPF got the job done for AWS. Those discussions probably sounded like a bunch of smart kids trying to measure outside temperature with a moist finger, so the only recommendation I could give in 2021 was “use the best tool for the job, keeping in mind you’re not Google or Microsoft”
It’s always better to measure than to have opinions, and a group of academics did just that. They developed Sybil – a tool to measure routing protocol performance in leaf-and-spine fabrics – and Dip Singh used it to compare BGP to IS-IS and OpenFabric.
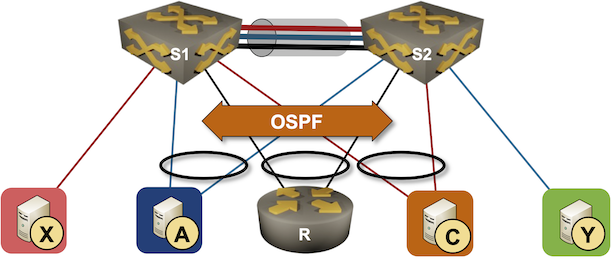
Running Routing Protocols over MLAG Links
It took vendors like Cisco years to start supporting routing protocols between MLAG-attached routers and a pair of switches in the MLAG cluster. That seems like a no-brainer scenario, so there must be some hidden complexities. Let’s figure out what they are.
We’ll use the familiar MLAG diagram, replacing one of the attached hosts with a router running a routing protocol with both members of the MLAG cluster (for example, R, S1, and S2 are OSPF neighbors).
… updated on Thursday, December 1, 2022 16:30 UTC
ICMP Redirects and Suboptimal Routing
A while ago, I wrote a blog post explaining why we should (mostly) disable ICMP redirects, triggering a series of comments discussing the root cause of ICMP redirects. A few of those blamed static routes, including:
Put another way, the presence or absence of ICMP Redirects is a red herring, usually pointing to architectural/design issues instead. In this example, using vPC Peer Gateway or, better yet, running a minimal IGP instead of relying on static routes eliminates ICMP Redirects from both the problem and solution spaces simultaneously.
Unfortunately, that’s not the case. You can get suboptimal routing that sometimes triggers ICMP redirects in well-designed networks running more than one routing protocol.
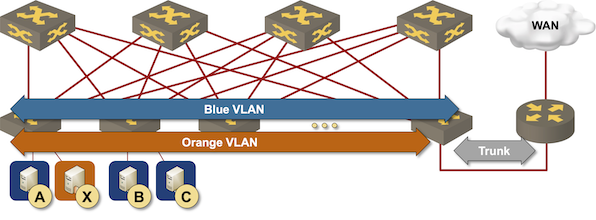
Integrated Routing and Bridging (IRB) Design Models
Imagine you built a layer-2 fabric with tons of VLANs stretched all over the place. Now the users want to exchange traffic between those VLANs, and the obvious question is: which devices should do layer-2 forwarding (bridging) and which ones should do layer-3 forwarding (routing)?
There are four typical designs you can use to solve that challenge:
- Exchange traffic between VLANs outside of the fabric (edge routing)
- Route on core switches (centralized routing)
- Route on ingress (asymmetric IRB)
- Route on ingress and egress (symmetric IRB)
This blog post is an overview of the design models; we’ll cover each design in a separate blog post.
Video: Routing Protocols Overview
After discussing network addressing and switching, routing, and bridging in the How Networks Really Work webinar, it was high time for a deep dive into routing protocols, starting (as always) with an overview.
Must Read: Routing Will Never Be a Solved Problem
Mark Seery wrote a fantastic must-read article explaining why routing will never be a solved problem.
You might want to enjoy it as a relaxing antidote after a painful exposure to SD-WAN (or SD-something-else) brainwashing.
