Blog Posts in January 2007
Cisco IOS web server with no enable password
Default username on Cisco routers
There are, however, a few things you can do if you want to relax the access to your router in a lab environment (never do it in a production network):
- If you configure no enable password, you can switch to enable mode without supplying a password
- If you want to telnet to a router without supplying a password, configure no login on the vty lines.
- If you want to be in privilege mode immediately after accessing the router, configure privilege level on the console or vty lines.
Firewalls kill TCP performance when faced with out-of-order packets
Today I've discovered another huge show-stopper: stateful firewalls (read: almost everything in use today) might just drop out-of-order packets, resulting in TCP timeouts and retransmissions (and repeated timeouts will totally wreck the session throughput). Here's how Cisco devices handle this problem:
- PIX allows three out-of-order packets per TCP session (cannot be changed, but should be enough)
- You can configure out-of-order packet handling on ASA with the queue-lenght parameter of a tcp-map .
- Cisco IOS firewall (formerly known as CBAC) drops out-of-order packets until release 12.4(11)T where you can use the ip inspect tcp reassembly configuration command (and it looks like the zone-based firewall configuration is not yet supported).
VTY access-class accepts extended and named access lists
These new features give you the ability to implement interesting policies, for example:
- Telnet access is only allowed from the network management station.
- SSH access is allowed from anywhere within internal network
You can also use the extended access list logging functionality, making it possible to log every connection attempt to the router.
Disable the "more" prompt
line consoleNote: this article is part of You've asked for it series.
length 0
line vty 0 4
length 0
Cisco IOS Login Enhancements
On top of that, the you can configure the router to enter quiet mode after several login failures have been detected in specified timeframe with the login block-for seconds attempts tries within seconds configuration command.
CEF punted packets
- If the destination is reachable over an interface that cannot use CEF-switching due to a feature not supported by CEF (for example, X.25 link), the packet has to be fast- or process-switched.
These destinations are easily discovered by inspecting the punt adjacencies).
- All packets destined for the router itself are process switched (thus punted).
- If the router needs to reply back to the source with an ICMP packet (redirect, unreachable ...), the reply can be generated only in the process-switching path.
- All packets with the IP options are punted to process switching.
- Fragments that have to be processed by the router are also process-switched.
This article is part of You've asked for it series.
CEF punt adjancency
In "border cases" you might find interesting CEF adjacencies in your CEF adjacency table (displayed with show ip cef adjacency). Most common one is the glean adjacency used for directly connected routes (this adjacency type is a placeholder that indicates the router it should perform the ARP table lookup and send the packet to directly connected neighbor). Discard, Drop, Noroute and Null adjacencies are obvious, the "weird" one is the Punt adjacency, which indicates that the router cannot CEF-switch the packet toward the destination (due to a feature being used that is not yet supported by CEF), thus the packet is punted to the next switching method (fast switching and ultimately process switching).
Reload the router from an interim privilege level
Count the logging messages
Per-Port CEF Load Balancing
In designs with very low number of IP hosts, no per-destination load-sharing algorithm will work adequately. Consider, for example, an extranet design where a large number of IP hosts are NAT-ed to a single IP address which then accesses a single remote server.
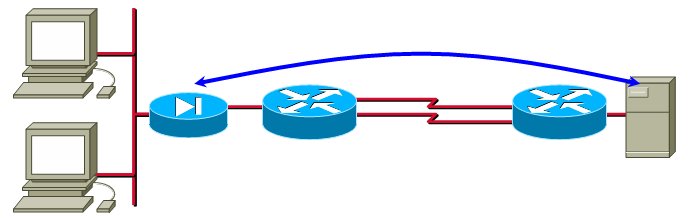
In this design, all the traffic flows between a single pair of IP addresses, making per-destination load-sharing unusable.
Improve the convergence of static routes
Enhanced OSPF Adjacency Logging
The log-adjacency-changes OSPF configuration command was improved with the detail command that logs every step of OSPF adjacency establishment (sample printout below), making it a great troubleshooting tool.
%OSPF-5-ADJCHG: Process 1, Nbr 172.16.0.21 on Serial0/0/0.100 from DOWN to INIT, Received Hello
%OSPF-5-ADJCHG: Process 1, Nbr 172.16.0.21 on Serial0/0/0.100 from INIT to 2WAY, 2-Way Received
%OSPF-5-ADJCHG: Process 1, Nbr 172.16.0.21 on Serial0/0/0.100 from 2WAY to EXSTART, AdjOK?
%OSPF-5-ADJCHG: Process 1, Nbr 172.16.0.21 on Serial0/0/0.100 from EXSTART to EXCHANGE, Negotiation Done
%OSPF-5-ADJCHG: Process 1, Nbr 172.16.0.21 on Serial0/0/0.100 from EXCHANGE to LOADING, Exchange Done
%OSPF-5-ADJCHG: Process 1, Nbr 172.16.0.21 on Serial0/0/0.100 from LOADING to FULL, Loading Done
How do I stop all logging done by the router
Note: this article is part of You've asked for it series.
Disable console logging
Update January 9th 2007: The router does not check if a user is logged into the console port or a device (for example, a terminal) is attached to it; if console logging is enabled, messages are always sent to the console port (causing CPU load).
To stop the console logging, use the no logging console global configuration command (highly recommended for routers that are not usually accessed through the console port) or you might want to limit the amount of messages sent to the console with the logging console level configuration command (for example, logging console notifications).
Note: this article is part of You've asked for it series.
"You've asked for it" series
So, to help my fellow networking engineers, I've decided to start a series of "You've asked for it" articles answering the questions that brought many of you to my site in the first place (and, don't forget, you can always send me an interesting question with the Send a message link on my bio page.
