Layer-3 Forwarding with VMware NSX Edge Services Router
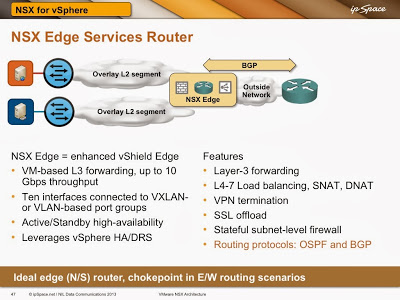
The easiest way of connecting overlay virtual networks implemented with VMware NSX for vSphere to the outside world is NSX Edge Services Router. It’s a much improved version of vShield Edge and provides way more than just layer-3 forwarding services – it’s also a firewall, load balancer, DHCP server, DNS forwarder, NAT and VPN termination device.
You can use a VMware NSX Edge Services Router (ESR) to connect multiple VXLAN-backed layer-2 segments within an application stack. You would configure the services router through NSX Manager (improved vShield Manager), and you’d get a VM connected to multiple VXLAN-based port groups (and probably one or more VLAN-based port groups) behind the scenes.
In this scenario, VXLAN kernel modules resident in individual vSphere hosts perform layer-2 forwarding, sending packets between VM and ESR NICs. ESR performs layer-3 forwarding within the VM context.
NSX Edge Services Router is the ideal solution when you need network services (firewalls, load balancers …) between the client and the server. It’s more than good enough for smaller deployments or when the majority of the traffic leaves the overlay virtual networking world (you can push up to 10 Gbps of traffic through it) … but don’t use it in high-volume environments with large amount of inter-subnet east-west traffic.
In those environments you might collapse multiple subnets into a single layer-2 segment (assuming your security engineers approve the change in security paradigm introduced with VM NIC firewalls) or use distributed routing functionality of VMware NSX. More about the latter in a follow-up blog post.
More information
- Watch VMware NSX Layer-3 Gateways video from NSX Architecture webinar;
- Overlay Virtual Networking webinar includes in-depth coverage of other virtual networking vendors.
- Cloud Computing Networking webinar covers even more topics, including over-the-cloud in hybrid cloud connectivity scenarios.

2 comments: