Category: BGP
On AI Agents Speaking BGP
I guess your LinkedIn feed is as full of AI nonsense as mine is, so I usually just skip all that posturing. However, every now and then, I stumble upon an idea that makes sense… until you start to dig deeper into it.
There was this post about AI agents speaking BGP with an associated GitHub repo, so I could go take a look at what it’s all about.
The proof-of-concept (so the post author) has two components:
MUST WATCH: BGP: the First 18 Years
If you’re at all interested in the history of networking, you simply MUST watch the BGP at 18: Lessons In Protocol Design lecture by Dr. Yakov Rekhter recorded in 2007 (as you can probably guess from the awful video quality) (HT: Berislav Todorovic via LinkedIn).
Using BIRD BGP Daemon as a BGP Route Reflector
In this challenge lab, you’ll configure a BIRD daemon running in a container as a BGP route reflector in a transit autonomous system. You should be familiar with the configuration concepts if you completed the IBGP lab exercises, but will probably struggle with BIRD configuration if you’re not familiar with it.
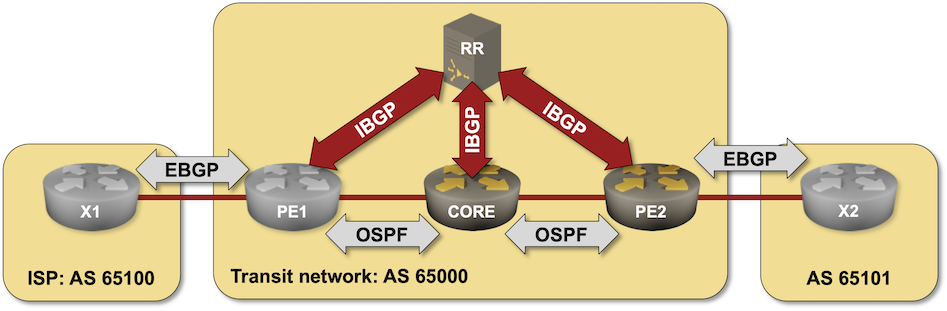
Click here to start the lab in your browser using GitHub Codespaces (or set up your own lab infrastructure). After starting the lab environment, change the directory to challenge/01-bird-rr, build the BIRD container with netlab clab build bird if needed, and execute netlab up.
Use Additional BGP Paths for IBGP Load Balancing
I wrote about the optimal BGP path selection with BGP additional paths in 2021, and I probably mentioned (in one of the 360 BGP-related blog posts) that you need it to implement IBGP load balancing in networks using BGP route reflectors. If you want to try that out, check out the IBGP Load Balancing with BGP Additional Paths lab exercise.
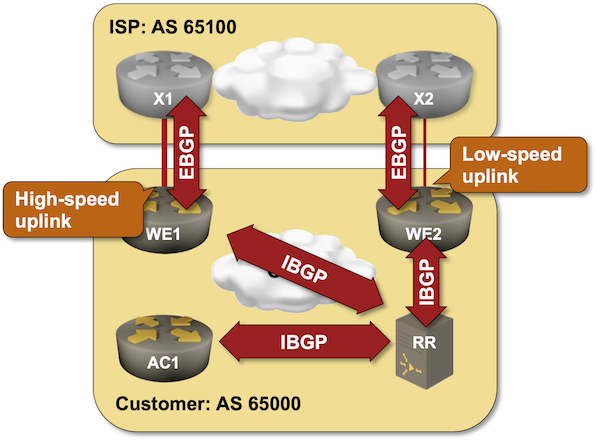
Click here to start the lab in your browser using GitHub Codespaces (or set up your own lab infrastructure). After starting the lab environment, change the directory to lb/4-ibgp-add-path and execute netlab up.
SwiNOG 40: When a Routing Control Functions Is Too Fresh
During integration testing, I find unexpected quirks in network devices way too often. However, that’s infinitely better than experiencing them in production (even after thoroughly testing stuff) while discovering that your peers don’t care about routing security, RPKI, and similar useless stuff.
For example, what happens if you define a new Routing Control Function (RFC) on Arista EOS and apply it to BGP routing updates in the same configuration session? You’ll find out in the Sorry We Messed Up (video) presentation Stefan Funke had at SwiNOG 40 (note: the bug has been fixed in the meantime).
iBGP Local-AS Route Propagation
In the previous blog post on this topic, I described the iBGP local-as functionality and explained why we MUST change the BGP next hop on the routes sent over the fake iBGP session (TL&DR: because we’re not running IGP across that link).
That blog post used a simple topology with three routers. Now let’s add a few more routers to the mix and see what happens.
Configuring BGP Community Propagation is Confusing
A large number of vendors claim to use industry-standard CLI, which means “something that looks like Cisco IOS, but we can’t say that in public.” The implementations of that “standard” are full of quirks; as I was making fun of Cisco IOS last week, it’s only fair to look at how others deal with BGP community propagation.
netlab has BGP configuration templates for 14 different platforms1, including these implementations that look like Cisco IOS from a distance if you squint just right2: Arista EOS, Aruba CX, and FRRouting. You can check the configuration templates if you wish; here’s the TC&DB3 overview:
BGP Community Propagation on Cisco IOS/XE: The 90's Called
Just when I thought no vendor stupidity peculiarity could surprise me, Cisco IOS/XE proved me wrong.
I was improving a completely unrelated BGP functionality. I ran BGP integration tests on Cisco IOL (because it’s the fastest one to boot), and the BGP community propagation test failed. After verifying that I did not change the template and that the data structures had not changed, I checked the IOL release I was using.
Surprise 🎉🎉: the neighbor send-community configurations that worked since (at least) the IOS Classic release 15.x stopped working in Cisco IOS/XE release 17.16.01a.
Worth Reading: BGP Unnumbered in 2025
Gabriel sent me a pointer to a blog post by Rudolph Bott describing the details of BGP Unnumbered implementations on Nokia, Juniper, and Bird.
Even more interestingly, Rudolph points out the elephant I completely missed: RFC 8950 refers to RFC 2545, which requires a GUA IPv6 next hop in BGP updates (well, it uses the SHALL wording, which usually means “troubles ahead”). What do you do if you’re running EBGP on an interface with no global IPv6 addresses? As expected, vendors do different things, resulting in another fun interoperability exercise.
Finally, there’s RFC 7404 that advocates LLA-only infrastructure links, so we might find the answer there. Nope; it doesn’t even acknowledge the problem in the Caveats section.
For even more information, read the Unnumbered IPv4 Interfaces and BGP in Data Center Fabrics blog posts.
iBGP Local-AS Next Hop Requirements
Did you know you could use the neighbor local-as BGP functionality to fake an iBGP session between different autonomous systems? I knew Cisco IOS supported that monstrosity for ages (supposedly “to merge two ISPs that have different AS numbers”) and added the appropriate tweaks1 into netlab when I added the BGP local-as support in release 1.3.1. Someone couldn’t resist pushing us down that slippery slope, and we ended with IBGP local-as implemented on 18 platforms (almost a dozen network operating systems).
I even wrote a related integration test, and all our implementations passed it until I asked myself a simple question: “But does it work?” and the number of correct implementations that passed the test without warnings dropped to zero.
Passive BGP Sessions
The Dynamic BGP Peers lab exercise gave you the opportunity to build a large-scale environment in which routers having an approved source IP addresses (usually matching an ACL/prefix list) can connect to a BGP route reflector or route server.
In a more controlled environment, you’d want to define BGP neighbors on the BGP RR/RS but not waste CPU cycles trying to establish BGP sessions with unreachable neighbors. Welcome to the world of passive BGP sessions.
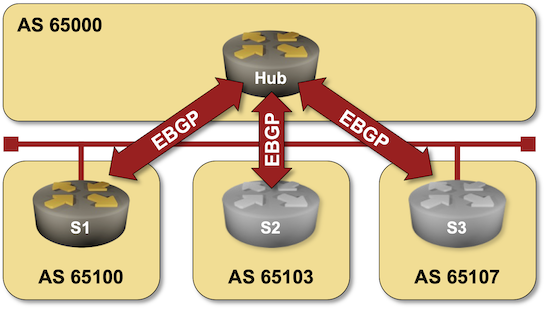
Click here to start the lab in your browser using GitHub Codespaces (or set up your own lab infrastructure). After starting the lab environment, change the directory to session/8-passive and execute netlab up.
Run BGP Across a Firewall
When I asked my readers what they would consider a good use case for EBGP multihop (thanks again to everyone who answered!), many suggested running BGP across a layer-3 firewall (Running BGP across a “transparent” (bump-in-the-wire) firewall is trivial). I turned that suggestion into a lab exercise in which you have to establish an EBGP multihop session across a “firewall” simulated by a Linux host.
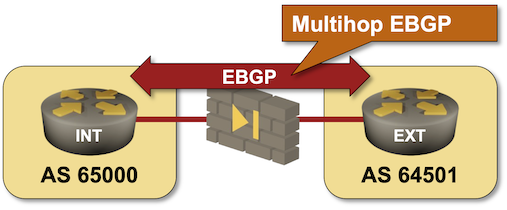
If you haven’t set up your own lab infrastructure, click here to start the lab in your browser using GitHub Codespaces. After starting your codespace, change the directory to basic/e-ebgp-multihop and execute netlab up.
The Curious Case of the BGP Connect State
I got this question from Paul:
Have you ever seen a BGP peer in the “Connect” state? In 20 years, I have never been able to see or reproduce this state, nor any mention in a debug/log. I am starting to believe that all the documentation is BS, and this does not exist.
The BGP Finite State Machine (FSM) (at least the one defined in RFC 4271 and amended in RFC 9687) is “a bit” hard to grasp but the basics haven’t changed from the ancient days of RFC 1771:
Use BGP Outbound Route Filters (ORF) for IP Prefixes
When a BGP router cannot fit the whole BGP table into its forwarding table (FIB), we often use inbound filters to limit the amount of information the device keeps in its BGP table. That’s usually a waste of resources:
- The BGP neighbor has to send information about all prefixes in its BGP table
- The device with an inbound filter wastes additional CPU cycles to drop many incoming updates.
Wouldn’t it be better for the device with an inbound filter to push that filter to its BGP neighbors?
IBGP Is the Better EBGP
Whenever I was explaining how one could build EBGP-only data center fabrics, someone would inevitably ask, “But could you do that with IBGP?”
TL&DR: Of course, but that does not mean you should.
Anyway, leaving behind the land of sane designs, let’s trot down the rabbit trail of IBGP-only networks.
