Dance around IOS bugs with Tcl and EEM
Recently, on an IPSec-based customer network, we installed one of the brand new platforms introduced by Cisco Systems. The initial software release had memory leaks (no problem, we all know these things happen), so we upgraded the box to the latest software. It works perfectly … until you reload it. The software we’re forced to use cannot get IPSec to work if the startup configuration includes interface-level crypto-maps. Interestingly, you can configure crypto-maps manually and they work … until you save them into the startup configuration and reload the box.
Things you cannot do with Tclsh
What would you think if you’d receive three queries about the same (somewhat obscure) feature within six hours? It started with a nice e-mail from an engineer that I’ve corresponded with in the past. He wanted to send a Wake-on-LAN packet to a PC in a remote office. Usually you could use the ip directed-broadcast feature, but he wanted to use the remote office router to generate the packet.
Decent DNS, DHCP and HTTP server on an ISR router
Readers of my blog have probably noticed that I’m occasionally documenting the shortcomings of DNS and DHCP servers built into Cisco IOS (I will not even mention the HTTP server, this one gets constantly degraded). On the other hand, although you could centralize all these services, the centralization makes the branch offices completely dependent on the availability of WAN uplinks; without a working uplink, a branch office stops completely.
The hidden wealth of IOS Tcl
Another undocumented (and thus very probably unsupported) Tcl-on-IOS detail: numerous Tcl packages are bundled with IOS and available in the tmpsys:lib/tcl directory (the tmpsys: is a virtual file system mapped to a part of the IOS image).
I need to slow down :)
I’ve just opened the January Technical Services News from Cisco. Nothing in there that would really interest me. Almost no routing protocols (one OSPF article), no BGP, no MPLS VPN. Based solely on this newsletter, one could get the feeling that I’m producing more documents covering core IP routing in a month than Cisco (I am positive that’s not the case).
But maybe Cisco’s engineers are refocusing on the new Support Wiki. Not really. After I’ve filtered out sequential changes to a single document, there were only 11 significantly changed documents in the Support Wiki in the last 30 days.
So I’m left wondering … what’s going on? Has everything already been written about the core IP routing features and the productive minds have shifted to voice and wireless? Are the engineers focused on IP routing becoming the dinosaurs? What’s your perspective?
But one thing is clear: I need to slow down.
Interactions between IP routing and QoS
One of my readers sent me an interesting question a while ago:
I reviewed one of your blog posts "Per-Destination or Per Packet CEF Load Sharing?" and wondered if you had investigated previously on how MQC QoS worked together with the CEF load-sharing algorithm (or does it interact at all)? For example, let's say I have two equal cost paths between two routers and the routing table (as well as CEF) sees both links as equal paths to the networks behind each router. On each link I have the same outbound service policy applied with a simple LLQ, BW, and a class-default queues. Does CEF check each IP flow and make sure both link's LLQ and BW queues are evenly used?
Unfortunately, packet forwarding and QoS are completely uncoupled in Cisco IOS. CEF performs its load balancing algorithm purely on source/destination information and does not take in account the actual utilization of outbound interfaces. If you have bad luck, most of the traffic ends on one of the links and the packets that would easily fit on the other link will be dropped by the QoS mechanisms.
You could use multilink PPP to solve the problem in low-speed environments. With MLPPP, CEF sends the traffic to a single output interface (the Multilink interface) and the queuing mechanisms evenly distribute packet fragments across the links in the bundle.
In high-speed environments, you can only hope that the number of traffic flows traversing the links will be so high that you’ll get a good statistical distribution (which is usually the case).
Flash-based DHCP database
Pete sent me an interesting question a while ago:
It might be interesting to write an article about ip dhcp database flash:dhcp-db command, documenting the pros of surviving a reboot versus cons of wear on the flash device.
I’ve already written about a few problems that can be solved with the DHCP database (but obviously a longer text is warranted … already stored in my to-do list) and it took me a while to find the time to dig out the relevant information on the flash device wear.
EBGP Multipath Load Sharing and CEF
When I was discussing the details of the BGP troubleshooting video with one of my readers, he pointed out that I should mention the need for CEF switching in EBGP multipath scenario. My initial response was “Why would you need CEF? EBGP multipath is older than CEF” and his answer told me I should turn on my gray cells before responding to emails: “Your video as well as Cisco’s web site recommends CEF for EBGP multipath design… but interestingly, it does work without CEF”.
The real reason we need CEF in EBGP load sharing designs is the efficacy of load distribution. Without CEF, the router will send all traffic toward a single BGP prefix over one of the links (fast switching performs per-destination-prefix load sharing). With CEF, the load is distributed based on the source-destination IP address pair combinations. Even if multiple clients send the traffic toward the same server, the load is spread across available links.
Generate HTTP(S) requests from Tcl shell
A few days ago, a reader sent me an e-mail titled “Telnet Automation from a Cisco Router” and complained that IOS Tcl does not support the expect commands (spawn, send and expect). Since Expect is a Tcl extension, not part of the core Tcl, it’s not included in Cisco IOS, which was the only answer I could give.
Can brain dumps be stopped?
Brain dumps are the biggest threat to the certification industry these days, significantly devaluing certifications that rely primarily on multiple-choice answers. Similarly to the threat-prevention measures adopted by airport security (read the insightful analysis of their behavior from Bruce Schneier, a renowned security guru), IT vendors are responding with high-tech measures.
Extranet with Overlapping Addresses
The idea to write an article describing how you can use MPLS VPN-enabled NAT to implement flexible extranets that allow participants to retain their existing (and sometimes overlapping) IP address space has been sitting in my to-do list for over a year.
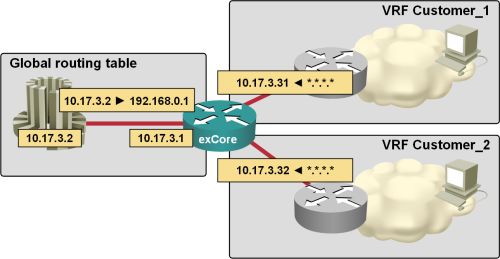
After I’ve finally written it (without even hinting what I’ve been working on), I got several e-mails from my readers asking the questions this article answers, so it looks like the topic has suddenly become very hot. Do you have any ideas why that would be the case?
You’ll find the original article somewhere in this list.
Test the real-life skills of your job candidates
Numerous companies use certifications to screen job candidates. Even if all the caveats associated with this process are given, you might encounter candidates who have multiple high-level certifications but cannot differentiate a router from a box of cheese. How can you identify (and reject) such people?
Is it wise to use certifications in the candidate selection process?
My previous certification-related post described how some companies use certifications to filter job applicants for networking-related positions. Should you follow that example? If you’re in a country with a saturated job market, where the number of applicants far exceeds the number of job postings (consider yourself very lucky if you’re an employer), you should certainly use whatever filters you can to screen the hundreds of applications you receive … but be aware that you have potentially lost a few gems hidden in the flood.
MPLS support on 1800-series routers
Christoph sent me an interesting question a few days ago:
I played a bit arround with 2 Cisco 1803 and I found MPLS related configurations commands in IOS 12.4(15)T (Advanced Enterprise) on this box. MPLS was not listed as a included fearture in the Cisco Feature Navigator for this image and some searching at cisco.com took me to a 2 year old document telling me that MPLS isn't supported on this series. Some more searching took me back to the Cisco Feature Navigator which lists MPLS as feature for the Cisco 1805 router (which uses the same IOS image, afaik).
So, I'm a bit confused now if MPLS is really working / supported on the low-end Cisco ISR 1800 fixed series?
MPLS was mostly available but never supported on low-end platforms (including Cisco 2600). In those days I've taken some heat for reusing existing 2600-based labs to teach Cisco-internal MPLS courses (since we were teaching the students to configure unsupported devices :).
Anyhow, the "not supported" means exactly that: it may be available (well, it is), it may work (it actually does), but if it's broken (and I've seen at least one low-end-platform-specific bug in the early days) you can't complain.
Is anyone aware whether the official support for the MPLS on 1800 series has changed? If so, please share your information with us.
If you need to offer a production-grade service to your customers, don't use unsupported equipment; if you need a solution for your personal needs or you're building a lab, go ahead.
Why would I need a Web Application Firewall?
If you have been visited by a friendly Cisco sales engineer recently, you might have already heard about the ACE Web Application Firewall (WAF). If you’re curious enough to start investigating on your own, you might have stumbled across the WAF product description on Cisco’s Web site, which tells you … nothing.
Let’s start with an easy question: if I already have a firewall, why would I need another box with “fire” and “wall” in its name? The short answer is “Because Web programmers rarely know how to write secure Web applications.”
