Use Slow IGP Startup in LDP-only MPLS Environments
If you use LDP-based MPLS as the only means of transporting data across your network core (for example, in MPLS VPN networks or in BGP-free ISP core), a router startup might disrupt your Label Switched Paths (remember: they are always based on IGP best paths) leading to a temporary disruption in service.
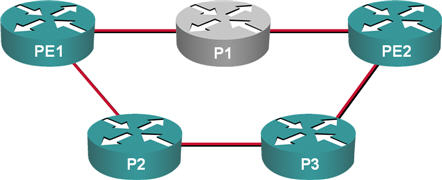
For example, when the router P1 in the network shown in the following diagram is powered on, and its IGP advertises its presence, the IGP-derived path from PE1 to PE2 will go over P1. If the LDP on P1 has not exchanged labels with PE1 and PE2, there will be no LSP on the shortest path between PE1 and PE2, resulting in a loss of traffic until the labels are exchanged and LSP is built.
The proper router startup timing in this environment is thus:
- Start IGP and find neighbors.
- Receive IGP updates and build the network topology.
- Start LDP and exchange labels for all prefixes in the network.
- Advertise the router’s presence in IGP.
You can configure slow OSPF startup with the max-metric router-lsa on-startup seconds router configuration command. The corresponding IS-IS command is set-overload-bit on-startup seconds.
The initial IGP delay has to be configured manually (you cannot use wait-for-bgp option in this scenario) and should take into account the time needed to:
- Find IGP neighbors (at least the hello timer);
- Receive LSA updates;
- Run SPF (at least the spf delay).
- Find LDP neighbors (at least the discovery hello interval).
- Exchange labels once the SPF run has been completed.
Unless you’re under very rigid time constraints, 30 seconds seems like a reasonable delay in most environments.

http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/sw/iosswrel/ps1829/products_feature_guide09186a00802d95dd.html
However some vendors such as Huawei had implemented it already.
Startup Manager
Slow Startup
Windows Startup
XP Startup