New look
Display open TCP and UDP ports
What is a BGP RIB failure
Sometimes you'll see a weird route status (RIB-failure) in your BGP table, for example:
GW#show ip bgp ¦ include r>
r> 10.2.0.0/16 10.0.1.2 0 0 65001 i
A more thorough investigation of the BGP entry does not give you a lot of additional information:
GW#show ip bgp 10.2.0.0
BGP routing table entry for 10.2.0.0/16, version 7
Paths: (1 available, best #1, table Default-IP-Routing-Table, RIB-failure(17))
Flag: 0x820
Advertised to update-groups:
1 2
65001
10.0.1.2 from 10.0.1.2 (10.0.1.2)
Origin IGP, metric 0, localpref 100, valid, external, best
The “mistery” is solved when you inspect the entry in the IP routing table:
GW#show ip route 10.2.0.0
Routing entry for 10.2.0.0/16
Known via "static", distance 1, metric 0 (connected)
Routing Descriptor Blocks:
* directly connected, via Null0
Route metric is 0, traffic share count is 1
The GW router has a static route that collides with the EBGP route and thus the BGP route cannot be inserted in the IP routing table (as the static route has administrative distance 1).
Let's conclude with a few interesting facts about the RIB failures:
- The RIB failure feature was introduced in IOS release 12.2T; prior to that, the BGP routes with higher administrative distance than other route sources were silently ignored (similar to all other routing protocols).
- You can display BGP routes that are not inserted in the IP routing table with the show ip bgp rib-failure command, which also explains why the BGP route was not inserted in the IP routing table.
- The BGP routes that are not used due to higher administrative distance are still advertised to all BGP peers (contrary to what most other distance-vector routing protocols do), unless you configure bgp suppress-inactive (introducted in 12.2T and 12.0(26)S).
EEM CLI patterns are not context sensitive
event manager applet NoReload… you cannot enter the action x.y reload configuration command any more (or any other command that includes the string reload).
event cli pattern "reload" sync no skip yes
To distinguish the reload command from other appearances of the same string, use the ^reload pattern (reload occuring at the beginning of the line).
Trivia: this actually occured to me when I was testing the setup described in the December IP Corner article. Sometimes we have to learn the hard way :)
Making the case for Layer 2 and Layer 3 VPNs
Occasionally someone would try to persuade me that the layer-2 VPN services are like aspirin (you know, totally harmless plus it could get rid of all your headaches). OK, that might be true if you take the layer-2 VPN offering as a pure transport solution and plug in an extra router (sometimes also called a layer-3 switch by marketing people) between the Service Provider’s Ethernet (or whatever they give you) and your LAN. But there are people who don’t know the details and plug the SP Ethernet straight into their L2 switch … and things might even work for a while … until the whole network collapses.
In my opinion, we need both L2 and L3 VPN services, but it’s important that they are positioned and deployed correctly. You can read more about my views on this topic in the SearchTelecom article Making the case for Layer 2 and Layer 3 VPNs.
MPLS Traffic Engineering without a Link State routing protocol
I remember being involved in a situation years ago (around the 12.0T release) where someone wanted to use MPLS TE without IS-IS (which was the only supported protocol in those days) and somehow the solution was to set up tunnels using explicit paths, where you have to specify hop-by-hop IP addresses. When you think about it, it makes perfect sense: if you list every IP address in the path, there is no need for constraint-based path calculation (PCALC). However, as it turns out, the later additions to MPLS TE (loose source routing, address exclusion, inter-area MPLS TE, inter-AS MPLS TE) changed the IOS code sufficiently that even the hop-by-hop tunnels cannot be set up without operational OSPF or IS-IS:
- In order to have MPLS TE running on a router, you need an MPLS TE router-id, and you can only specify that in OSPF or IS-IS routing protocol.
- Even though the hop-by-hop explicit path is static, the router wants to run PCALC for every hop in the path. If the next-hop IP address is not in the OSPF topology database, the router will not even try to set up the tunnel.
If you want to run MPLS TE in your network, you thus need to run OSPF or IS-IS, even though you might not want to use them for IP packet forwarding. For example, you could enable one of them only on the links actually used for MPLS TE and set the distance to 255 to prevent their routes from getting into the IP routing table (and I've tested it in the lab before writing this post).
Mandatory EEM CLI commands
The action cli commands used in EEM applets as well as the cli* Tcl functions used in EEM Tcl policies open a virtual Telnet session to a VTY line to execute the CLI commands. The first command you have to execute in the EEM applet is thus the enable command to ensure the next commands will be executed with privilege level 15.
You don't have to specify the enable password.
Likewise, if you want to configure the router, the next command to execute is the configure terminal command, followed by the configuration commands.
BGP fast session deactivation also speeds up session establishment
03:28:42: RT: add 10.0.3.3/32 via 10.2.0.2, ospf metric [110/75]
03:28:42: RT: NET-RED 10.0.3.3/32
03:28:44: RT: Try lookup less specific 10.0.3.3/32, default 1
03:28:44: RT: Found subnet on less specific 10.0.3.3/32
03:28:44: %BGP-5-ADJCHANGE: neighbor 10.0.3.3 Up
Execute CLI commands with prompts in EEM
By default, the EEM action cli command waits until it receives exec-level prompt from the VTY (Router> or Router#), resulting in an endless wait and aborted EEM applet in IOS release 12.4(15)T (earlier releases would hang a VTY line forever) if a CLI command returns an additional prompt. With the pattern option, you can change the expected reply to whatever prompt the CLI command is outputting.
BGP without MPLS?
As I know some of you run large networks, could you help me understand what you're using (without giving away too much information, of course):
- Are you running a BGP network without MPLS or are you using BGP on the edges and MPLS transport in the core?
- If you have a large number of BGP routers, do you have a nice hierarchy of BGP route reflectors (or confederations) or ad-hoc implementation where every router has all neighbors as RR-clients?
Full disclosure: I might use the information you give me in an upcoming article.
BGP Fast Session Deactivation
We all know that BGP is meant to converge slowly… well, the MPLS/VPN service providers tend to disagree, as their users are not used to minute-long convergence times. One of the major components of slow BGP convergence is the time it takes a router to discover that a neighbor has disappeared. Traditionally, the BGP keepalive packets were sent every minute and it took up to three minutes to discover that a neighbor is down.
Of course you could fine-tune those times with the neighbor timers configuration command, but the reduced timers resulted in increased TCP traffic and consequently increased CPU load, which could reach tens of percents if the timers were set to a few seconds and the router had lots of BGP neighbors.
Configure DNS Servers Through IPCP
After I've fixed the default routing in my home office, I've stumbled across another problem: the two ISPs I'm using for my primary and backup link have DNS servers that reply solely to the DNS requests sent from their own IP address range:
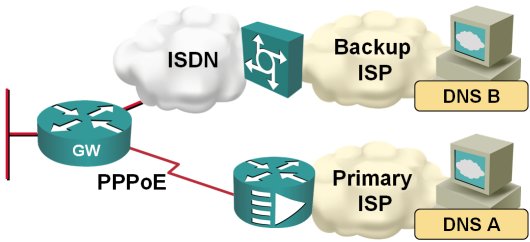
When the traffic is switched from the primary to the backup ISP, I therefore also need to switch the DNS servers. Fortunately, this is quite easy to do on a router; you just need to configure ppp ipcp dns request on the dialer interface and the router starts asking for the DNS server address as part of the IPCP negotiation.
Enhanced show interfaces command
It's amazing how many options (most of them still undocumented) the show interfaces command accepts in IOS release 12.4T (I won't even start guessing when each one was introduced, if you're running old IOS releases, please feel free to comment):
- show interfaces description displays interface names, L1 and L2 status (line and line-protocol status) and interface description. Extremely handy if you want to check which interfaces are up/down.
- show interfaces counters protocol status displays the L3 protocols active on each interface.
- show interfaces summary displays the state of various interface queues and related drop counters in a nice tabular format.
- show interfaces accounting displays per-protocol in/out counters.
Here are a few sample printouts:
Can I combine EEM applets with Tcl shell?
When I’ve been describing the limitations of kron, someone quickly asked an interesting question:
As I cannot insert extra input keystrokes with EEM applet, can I run a Tcl script from it with the action sequence cli command “tclsh script” command and use the typeahead function call to get around the limitation?”
The only answer I could give at that time was “maybe” … and obviously it was time for a more thorough test. The short result is: YES, you can do it (at least in IOS release 12.4(15)T1).
Kron: poor-man's cron
When two groups within Cisco needed time-based command execution in Cisco IOS, they (in a typical big-corporation fashion) decided to implement the same wheel from two different sets of spokes and rims. One group built the Embedded Event Manager with its event timer cron command (introduced in 12.2(25)S and 12.3(14)T), the other group created the more limited kron command set (introduced in 12.3(1)).
