Enhanced show interfaces command
It's amazing how many options (most of them still undocumented) the show interfaces command accepts in IOS release 12.4T (I won't even start guessing when each one was introduced, if you're running old IOS releases, please feel free to comment):
- show interfaces description displays interface names, L1 and L2 status (line and line-protocol status) and interface description. Extremely handy if you want to check which interfaces are up/down.
- show interfaces counters protocol status displays the L3 protocols active on each interface.
- show interfaces summary displays the state of various interface queues and related drop counters in a nice tabular format.
- show interfaces accounting displays per-protocol in/out counters.
Here are a few sample printouts:
Can I combine EEM applets with Tcl shell?
When I’ve been describing the limitations of kron, someone quickly asked an interesting question:
As I cannot insert extra input keystrokes with EEM applet, can I run a Tcl script from it with the action sequence cli command “tclsh script” command and use the typeahead function call to get around the limitation?”
The only answer I could give at that time was “maybe” … and obviously it was time for a more thorough test. The short result is: YES, you can do it (at least in IOS release 12.4(15)T1).
Kron: poor-man's cron
When two groups within Cisco needed time-based command execution in Cisco IOS, they (in a typical big-corporation fashion) decided to implement the same wheel from two different sets of spokes and rims. One group built the Embedded Event Manager with its event timer cron command (introduced in 12.2(25)S and 12.3(14)T), the other group created the more limited kron command set (introduced in 12.3(1)).
Install default route with PPP
In my home office, I'm using DSL access to the Internet with ISDN backup to another ISP, as shown on the next figure:
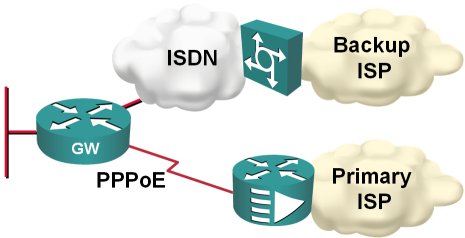
Obviously, I would like the ISDN backup to kick in whenever the primary connection goes down; two static default routes and reliable static routing on the primary default seem like a perfect solution.
Enable password or enable secret?
- Type-7 encryption used in enable password has been broken. Source code for the decrypt program and cracker programs are available online, or you could use a router to do it for you.
- The type-7 encryption is reversible (and easily breakable due to a weak algorithm), whereas type-5 encryption is a one-way encryption that probably requires a dictionary attack to break.
- Based on the previous two facts, you should never use enable password. Use enable secret.
- The service password-encryption encodes passwords attached to local usernames with type-7 encryption. The usage of type-7 encryption is necessary as you might need the cleartext passwords in some authentication mechanisms (for example, CHAP). However, it's still better to have scrambled passwords than cleartext ones; at least a casual observer will not be able to read them. Conclusion: use service password-encryption.
- If your authentication methods don't need cleartext passwords (examples: local username/password authentication, local AAA authentication or PAP authentication), use username secret configuration command (available from IOS releases 12.2T, 12.3 and 12.0S).
Emulate dialup links with serial lines
interface Serial1/0… and this is the “server”-side configuration:
ip address negotiated
encapsulation ppp
ppp authentication pap optional
ppp pap sent-username client password 0 client
interface Serial1/0To trigger PPP negotiations, shut down and re-enable the serial interface on either side.
ip address 10.0.0.33 255.255.255.252
encapsulation ppp
peer default ip address 10.0.0.34
ppp authentication pap callin
!
username client password client
Note: As I'm using PAP authentication, I could use the more secure username secret configuration command, which would not work with CHAP.
IPv6 Deployment: Time for Action?
A while ago I was asked to write an article about IPv6 training. I could just cover the training aspect, like what’s offered (answer: not much) and whether someone can train the whole operations team like you could in the IPv4 or MPLS/VPN world (answer: no), but I wanted to understand whether anyone is really using IPv6 in a production network.
I found a few academic networks (after all, there are about 2000 IPv6 prefixes assigned and someone should be doing something with them), but not much of what I would call a real production environment, which is a bad thing, as it looks like the IPv4 address space will get saturated in a few years.
Use BGP Default Route to Replace Static Routing
Martin Kluge sent me an interesting BGP question: he has two upstream links and runs BGP on both. Since his router is low on RAM, he cannot accept full routing, so he’s just announcing his IP prefix and using static default routing toward upstream ISPs.
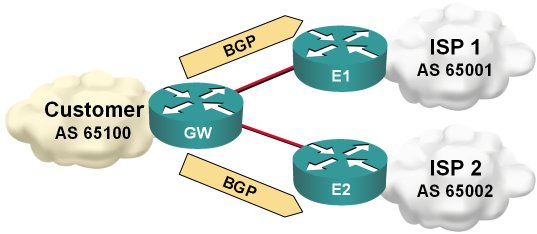
Static default routing toward upstream ISP
Type 7 decryption in Cisco IOS
We'll turn on type-7 encryption for local passwords and generate a test username
R1(config)#service password-encryption
R1(config)#username test password t35t:pa55w0rd
Next we'll inspect the generated username with the show running command
R1(config)#do show run | include username
username test password 7 08351F1B1D431516475E1B54382F
Now we'll create a key chain and enter the type-7 encrypted password as the key string …
R1(config)#key chain decrypt
R1(config-keychain)#key 1
R1(config-keychain-key)#key-string 7 08351F1B1D431516475E1B54382F
… and the show command does the decryption for us.
R1(config-keychain-key)#do show key chain decrypt
Key-chain decrypt:
key 1 -- text "t35t:pa55w0rd"
accept lifetime (always valid) - (always valid) [valid now]
send lifetime (always valid) - (always valid) [valid now]
Show active IOS processes
- The [0-9.]+% pattern will match any non-zero percentage;
- The 0.00% pattern will obviously match the zero-percentage display;
- As the percentage figures are separated by various amounts of whitespace characters, we have to use the ' +' pattern to match those;
Persistent EEM variables
The real solution is based on the appl_setinfo and appl_reqinfo calls. They work, but like many other Tcl-related IOS features they are … well … weird.
Ones Are Slower than Zeroes
Thinking about the implications of bit stuffing I wrote about in the SDLC post, I realized that long sequences of ones would be transmitted slower than long sequences of zeroes due to an extra bit being inserted after every fifth consecutive one. The theory would predict a 20% decrease in transmission speed.
Of course I wanted to test this phenomenon immediately. I connected two routers with a low-speed (64 kbps) link, and started a series of pings. Not surprisingly, the results confirmed the theory:
Impact of Netflow accounting
The link to this white paper has been published in Joe Harris' blog.
