netlab: Combining VLANs with VRFs
Last two weeks we focused on access VLANs and VLAN trunk netlab implementation. Can we combine them with VRFs? Of course.
The trick is very simple: attributes within a VLAN definition become attributes of VLAN interfaces. Add vrf attribute to a VLAN and you get all VLAN interfaces created for that VLAN in the corresponding VRF. Can’t get any easier, can it?
How about extending our VLAN trunk lab topology with VRFs? We’ll put red VLAN in red VRF and blue VLAN in blue VRF.
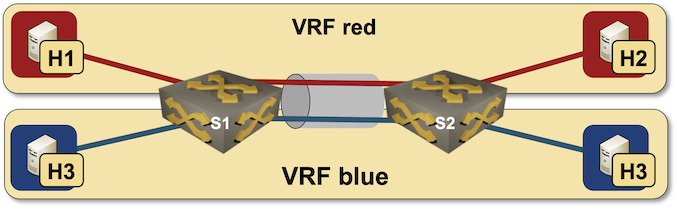
Combining VLANs with VRFs
We’ll take the existing VLAN trunk lab topology and modify it a bit. First, we have to enable VRF support on the switches – we’ll add vrf module to the list of modules used by S1 and S2.
groups:
switches:
members: [ s1, s2 ]
module: [ vlan,vrf ]
device: eos
Next, we have to define the VRFs.
vrfs:
red:
blue:
Finally, a bit of magic dust: add vrf attribute to VLAN definitions:
vlans:
red:
vrf: red
blue:
vrf: blue
That’s it. Execute netlab up1 (after downloading the final topology file) and you’ll have a multi-VRF lab using a VLAN trunk.
Here are the relevant parts of Arista cEOS configuration in case you’re wondering what we achieved with the few extra lines in lab topology file:
spanning-tree mode mstp
!
vlan 1000
name red
!
vlan 1001
name blue
!
vrf instance blue
rd 65000:2
!
vrf instance red
rd 65000:1
!
interface Ethernet1
mac-address 52:dc:ca:fe:05:01
switchport access vlan 1000
!
interface Ethernet2
mac-address 52:dc:ca:fe:05:02
switchport access vlan 1001
!
interface Ethernet3
description s1 -> s2
mac-address 52:dc:ca:fe:05:03
switchport trunk allowed vlan 1000-1001
switchport mode trunk
!
interface Vlan1000
description VLAN red (1000) -> [h1,s2,h2]
vrf red
ip address 172.16.0.5/24
!
interface Vlan1001
description VLAN blue (1001) -> [h3,s2,h4]
vrf blue
ip address 172.16.1.5/24
!
ip routing
ip routing vrf blue
ip routing vrf red
Want to run this lab on your own, or try it out with different devices? No problem:
- Install netlab
- Download the relevant containers or create Vagrant boxes
- Download the topology file into an empty directory
- Execute netlab up
- Enjoy! 😊
-
Assuming you completed your homework and created a Ubuntu VM, installed the software, and downloaded Arista cEOS container. ↩︎
