On Routing Protocol Metrics
This LinkedIn snippet just came in from the someone is not exactly right on the Internet department:
Unlike IGP protocols, BGP is not dependent on a single type of metric to choose the best path.
EIGRP is an immediate counterexample that brought the above quote to my attention, but it’s worth exploring the topic in more detail.
Upcoming BGP Labs, 2024 Edition
It’s that time of the year when we create unreachable goals and make empty promises to ourselves (or others) that we subconsciously know we’ll fail.
I tried to make that process a bit more structured and create external storage for my lab ideas – I started publishing more details on future BGP lab scenarios. The lab descriptions contain a high-level overview of the challenge and the lab topology; the details will be filled in later.
Want to know what’s coming in 2024? Check out the Upcoming Labs page of the BGP Labs project.
Public Cloud Networking Hands-On Exercises
I got this request from someone who just missed the opportunity to buy the ipSpace.net subscription (or so he claims) earlier today
I am inspired to learn AWS advanced networking concepts and came across your website and webinar resources. But I cannot access it.
That is not exactly true. I wrote more than 4000 blog posts in the past, and some of them dealt with public cloud networking. There are also the free videos, some of them addressing public cloud networking.
Goodbye, ipSpace.net Subscription
I ran the first webinar as an independent author almost exactly fourteen years ago1, with the first ticket sold just before New Year’s Eve. I kept focusing on individual webinars until someone asked me, “Would it be possible to buy access to everything you did?” His question effectively created the ipSpace.net subscription, with the first one sold in late 2010 (I still have the email that triggered the whole process).
End-of-Year Cleanup: OSPF Blog Posts
After procrastinating for months, I finally spent a few days cleaning up and organizing OSPF blog posts (it turns out I wrote almost 100 blog posts on the topic in the 18 years of blogging).
Setting Source IP Address on Traffic Started by a Multihomed Host
In the Path Failure Detection on Multi-Homed Servers blog post, I mentioned running BGP on servers as one of the best ways to detect server-to-network failures. As always, things aren’t as simple as they look, as Cathal Mooney quickly pointed out:
One annoyance is what IP address gets used by default by the system for outbound traffic. It would be nice to have a generic OS-level way to say, “This IP on lo0 should be default for outbound IP traffic unless to the connected link subnet itself.”
That’s definitely a tough nut to crack, and Cathal described a few solutions he used in the past:
BGP Challenge: Merge Autonomous Systems
Here’s a challenge in case you get bored during the Christmas break: merge two networks running BGP (two autonomous systems) without changing anything but the configurations of the routers connecting them (the red BGP session in the diagram). I won’t give you any hints; you can discuss it in the comments or a GitHub discussion.
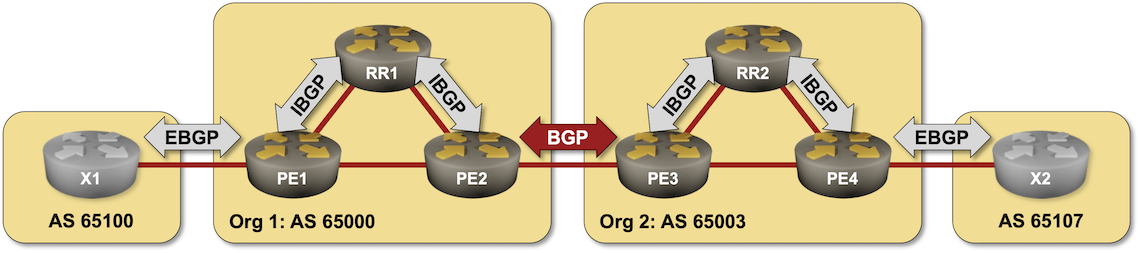
Hopefully, you won’t have to deal with something similar in real life, but then we know that crazy requirements trump good designs any day of the week.
Review: Unnumbered Interfaces in netlab
A while ago, Chris Parker published a nice blog post explaining how to configure unnumbered interfaces with IS-IS in Junos. It’s well worth reading, but like my Unnumbered Ethernet Interfaces blog post, it only covers one network operating system. What if you want to do something similar on another platform?
How about using the collective efforts of the team developing device configuration templates for netlab? As of December 2023 netlab supports:
Worth Reading: The AI Supply Paradox
Eric Hoel published a spot-on analysis of AI disruptiveness, including this gem:
The easier it is to train an AI to do something, the less economically valuable that thing is. After all, the huge supply of the thing is how the AI got so good in the first place.
TL&DR: AI can easily disrupt things that are easy to generate and thus have little value. Seeing investors trying to recoup the billions pouring into the latest fad will be fun.
Worth Reading: State-of-the-Art AI
Gerben Wierda published another AI-buster article describing what exactly “state-of-the-art” means in AI benchmarks.
Hint: you give an AI model 32 step-by-step examples before asking a question, and it still gets it wrong 10% of the time.
Video: Language Model Basics
After a brief introduction of how the language models fit into the AI/ML landscape, Javier Antich explained the language model basics, including auto-regression, types of language models, the specifics of large language models, and potential use cases,
netlab: Version-Specific Topology Files
TL&DR: If you’re using netlab to build labs for your personal use, you can skip this one, but if you plan to use it to create training labs (like my BGP labs project), you might want to keep reading.
Like any complex enough tool, netlab eventually had to deal with inconsistent version-specific functionality and configuration syntax (OK, topology attributes). I stumbled upon this challenge when I wanted to make labs that use two types of configurable devices.
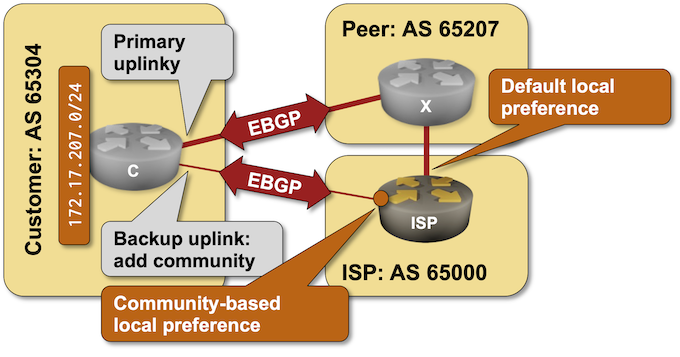
BGP Labs: Use BGP Communities in a Routing Policy
A previous BGP lab focused on the customer side of BGP communities: adding them to BGP updates to influence upstream ISP behavior. Today’s lab focuses on the ISP side of the equation: using BGP communities in a routing policy to implement RFC 1998-style behavior.
Interviewing a Network Engineer Using a Single Scenario
I always said that the Trivia Pursuit certification tests (or job interviews) are nonsense and that one should focus on fundamentals.
In a recent blog post, Daniel Dib described a fantastic scenario: using a simple “why can’t I connect to a web site” question, explore everything from ARP/ND to DNS and TLS.
Obviously, you’ll never see anything that sane in a certification test. An interactive interview doesn’t scale (beyond CCDE), and using humans (and common sense judgment) creates potential legal liabilities (there were rumors that had been one of the reasons a talk with a proctor who could flunk you was dropped from the CCIE test).
Response: Vendor Network Automation Tools
Drew Conry-Murray published a excellent summary of his takeaways from the AutoCon0 event, including this one:
Most companies want vendor-supported tools that will actually help them be more efficient, reduce human error, and increase the velocity at which the network team can support new apps and services.
Yeah, that’s nothing new. Most Service Providers wanted vendors to add tons of nerd knobs to their products to adapt them to existing network designs. Obviously, it must be done for free because a vast purchase order1 is dangling in the air. We’ve seen how well that worked, yet learned nothing from that experience.
