Creating MPLS/VPN Labs With netlab
Two week ago I described how to create a simple VRF Lite lab with netlab VRF configuration module. Adding MPLS/VPN to the mix and creating a full-blown MPLS/VPN lab is a piece of cake. In this blog post we’ll build a simple topology with two VRFs (red and blue) and two PE-routers:
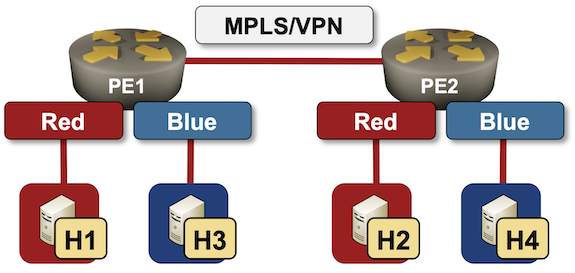
Lab topology
Nodes
We’ll need six nodes in the lab. Four of them will be Linux hosts, the two PE-routers will be Arista EOS devices. We’ll have to enable these configuration modules on the PE-routers:
vrffor obvious reasonsbgpbecause it’s needed to transport VPNv4 address family updates between PE-routersmplsto get LDP and BGP VPNv4 address familyospfbecause we’re building an IBGP design and need something to propagate loopback interface addresses.
defaults.device: eos
nodes:
pe1:
module: [ vrf,ospf,bgp,mpls ]
pe2:
module: [ vrf,ospf,bgp,mpls ]
h1:
device: linux
h2:
device: linux
h3:
device: linux
h4:
device: linux
We’ll use two VRFs, and let the tool automatically assign route distinguishers and route targets.
vrfs:
red:
blue:
Links
There are five links in our lab, four of them belong to VRFs, the fifth one connects PE1 and PE2:
links:
- pe1: { vrf: red }
h1:
- pe2: { vrf: red }
h2:
- pe1: { vrf: blue }
h3:
- pe2: { vrf: blue }
h4:
- pe1-pe2
Module Parameters
All we need now is a sprinkle of unicorn dust module parameters:
- BGP AS number is set to 65000
- LDP and VPNv4 are enabled within the MPLS module
bgp.as: 65000
mpls.ldp: True
mpls.vpn: True
And that’s it. Save the topology file into an empty directory, execute netlab up and you’ll have a full-blown MPLS/VPN lab.
Sample Configuration
Don’t trust me? Here are a few printouts:
pe1#show ip bgp vrf red
BGP routing table information for VRF red
Router identifier 10.0.0.1, local AS number 65000
Route status codes: s - suppressed, * - valid, > - active, E - ECMP head, e - ECMP
S - Stale, c - Contributing to ECMP, b - backup, L - labeled-unicast
% - Pending BGP convergence
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
RPKI Origin Validation codes: V - valid, I - invalid, U - unknown
AS Path Attributes: Or-ID - Originator ID, C-LST - Cluster List, LL Nexthop - Link Local Nexthop
Network Next Hop Metric AIGP LocPref Weight Path
* > 172.16.0.0/24 - - - - 0 i
* > 172.16.1.0/24 10.0.0.2 0 - 100 0 i
pe1#show ip route vrf red | begin Gateway
Gateway of last resort is not set
C 172.16.0.0/24 is directly connected, Ethernet1
B I 172.16.1.0/24 [200/0] via 10.0.0.2/32, LDP tunnel index 1, label 100000
via 10.1.0.2, Ethernet3, label imp-null(3)
pe1#show mpls lfib route
MPLS forwarding table (Label [metric] Vias) - 3 routes
MPLS next-hop resolution allow default route: False
...
B3 100000 [0]
via I, ipv4, vrf blue
B3 100001 [0]
via I, ipv4, vrf red
L 116384 [1], 10.0.0.2/32
via M, 10.1.0.2, pop
payload autoDecide, ttlMode uniform, apply egress-acl
interface Ethernet3
Finally, here are the relevant parts of PE1 configuration as generated by netlab release 1.2.1:
vrf instance blue
rd 65000:2
!
vrf instance red
rd 65000:1
!
!
interface Ethernet1
description pe1 -> [h1] [stub]
vrf red
ip address 172.16.0.1/24
ip ospf network point-to-point
ip ospf area 0.0.0.0
!
interface Ethernet2
description pe1 -> [h3] [stub]
vrf blue
ip address 172.16.2.1/24
ip ospf network point-to-point
ip ospf area 0.0.0.0
!
interface Ethernet3
description pe1 -> pe2
ip address 10.1.0.1/30
mpls ldp interface
ip ospf network point-to-point
ip ospf area 0.0.0.0
!
interface Loopback0
ip address 10.0.0.1/32
mpls ldp interface
ip ospf area 0.0.0.0
!
ip routing
ip routing vrf blue
ip routing vrf red
!
mpls ip
!
mpls ldp
router-id 10.0.0.1
transport-address interface Loopback0
interface disabled default
no shutdown
!
router bgp 65000
router-id 10.0.0.1
bgp advertise-inactive
neighbor 10.0.0.2 remote-as 65000
neighbor 10.0.0.2 next-hop-self
neighbor 10.0.0.2 update-source Loopback0
neighbor 10.0.0.2 description pe2
neighbor 10.0.0.2 send-community standard extended
!
address-family ipv4
neighbor 10.0.0.2 activate
network 10.0.0.1/32
!
address-family vpn-ipv4
neighbor 10.0.0.2 activate
!
vrf blue
rd 65000:2
route-target import vpn-ipv4 65000:2
route-target export vpn-ipv4 65000:2
router-id 10.0.0.1
redistribute connected
redistribute ospf
!
vrf red
rd 65000:1
route-target import vpn-ipv4 65000:1
route-target export vpn-ipv4 65000:1
router-id 10.0.0.1
redistribute connected
redistribute ospf
!
router ospf 1
router-id 10.0.0.1
max-lsa 12000
!
router ospf 100 vrf red
router-id 10.0.0.1
interface unnumbered hello mask tx 0.0.0.0
passive-interface Ethernet1
redistribute bgp
max-lsa 12000
!
router ospf 101 vrf blue
router-id 10.0.0.1
interface unnumbered hello mask tx 0.0.0.0
passive-interface Ethernet2
redistribute bgp
max-lsa 12000
Build Your Own
You’ll find the lab topology file on GitHub. To use it:
- Install netlab and your preferred lab environment. These days I find it easiest to use Arista cEOS with containerlab.
- Copy topology files into an empty directory
- Execute netlab up with the parameters described above.
Revision History
- 2024-08-10
- MPLS data plane works in cEOS release 4.32.1F and is supported in netlab release 1.9.0. Removed a mention of cEOS data-plane quirks.

Thank you for your work on this project!
Hope you'll find it useful... and if there's some functionality you'd love to see implemented just open a GitHub issue.