… updated on Monday, December 28, 2020 12:35 UTC
Load Balancing with Parallel EBGP Sessions
Establishing parallel EBGP sessions across parallel links between two edge routers (EBGP peers) – as displayed in the diagram below – is the most versatile form of EBGP load balancing. It does not require static routing or extra routing protocol (like the design running EBGP between routers’ loopback interfaces), device-specific tricks like configuring the same IP address on multiple interfaces) or specific layer-2 encapsulation (like Ethernet LAG or Multilink PPP).
It even allows proportional load-balancing across unequal-bandwidth links and combinations of various layer-2 technologies (for example, load-balancing between a serial line and an Ethernet interface). The only drawback of this design is the increased size of the BGP table, as every BGP prefix is received from the EBGP neighbor twice.
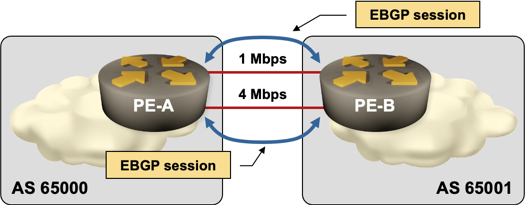
Parallel EBGP sessions
Benefits
- No extra routing protocol between EBGP neighbors
- Reliably detects link and node failures
- No IP addressing tricks
- No dependency on layer-2 transport technology
- Load balancing proportional to link bandwidth
Drawbacks
- Duplicate entries in the BGP table increase memory requirements
- Additional BGP session and larger BGP table increases CPU utilization
Basic configuration
To implement parallel EBGP sessions, configure multiple neighbors on both EBGP routers, one for each IP subnet (parallel link between the EBGP peers) and enable EBGP multipath load balancing with the maximum-paths router configuration command. Sample router configurations are shown below:
hostname PE-A
!
interface Loopback0
ip address 10.0.1.1 255.255.255.255
!
interface Serial1/4
description Link #1 to PE-B
bandwidth 1000
ip address 10.0.7.37 255.255.255.252
encapsulation ppp
!
interface Serial1/5
description Link #2 to PE-B
bandwidth 4000
ip address 10.0.7.45 255.255.255.252
encapsulation ppp
!
router bgp 65000
no synchronization
bgp log-neighbor-changes
neighbor 10.0.7.38 remote-as 65001
neighbor 10.0.7.46 remote-as 65001
maximum-paths 8
hostname PE-B
!
interface Loopback0
ip address 10.0.1.5 255.255.255.255
!
interface Serial1/0
description Link #1 to PE-A
bandwidth 1000
ip address 10.0.7.38 255.255.255.252
encapsulation ppp
!
interface Serial1/1
description Link #2 to PE-A
bandwidth 4000
ip address 10.0.7.46 255.255.255.252
encapsulation ppp
!
router bgp 65001
no synchronization
bgp log-neighbor-changes
neighbor 10.0.7.37 remote-as 65000
neighbor 10.0.7.45 remote-as 65000
maximum-paths 8
After the neighbors have been configured, inspect the BGP neighbor table with the show ip bgp summary command. All parallel sessions should be operational.
PE-A#show ip bgp summary | begin Neighbor
Neighbor V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent TblVer InQ OutQ Up/Down State/PfxRcd
10.0.7.38 4 65001 4 4 2 0 0 00:01:24 1
10.0.7.46 4 65001 4 4 2 0 0 00:01:24 1
Check the prefixes advertised by the EBGP peer with the show ip bgp prefix and show ip route prefix commands:
PE-A#show ip bgp 10.2.2.0
BGP routing table entry for 10.2.2.0/24, version 2
Paths: (2 available, best #1, table default)
Multipath: eBGP iBGP
Flag: 0x1820
Advertised to update-groups:
1
65001
10.0.7.38 from 10.0.7.38 (10.0.1.5)
Origin IGP, metric 0, localpref 100, valid, external, multipath, best
65001
10.0.7.46 from 10.0.7.46 (10.0.1.5)
Origin IGP, metric 0, localpref 100, valid, external, multipath
PE-A#show ip route 10.2.2.0
Routing entry for 10.2.2.0/24
Known via "bgp 65000", distance 20, metric 0
Tag 65001, type external
Last update from 10.0.7.46 00:00:10 ago
Routing Descriptor Blocks:
10.0.7.46, from 10.0.7.46, 00:00:10 ago
Route metric is 0, traffic share count is 1
AS Hops 1
Route tag 65001
* 10.0.7.38, from 10.0.7.38, 00:00:10 ago
Route metric is 0, traffic share count is 1
AS Hops 1
Route tag 65001
Bandwidth-proportional load balancing
Configure DMZ Link Bandwidth feature to enable load balancing proportional to the bandwidth of the parallel links:
- Configure neighbor ip-address dmzlink-bw on all EBGP sessions with the EBGP peer router.
- Configure proportional load sharing with the bgp dmzlink-bw router configuration command.
Modifications to the PE-A router configuration are shown below:
router bgp 65000
bgp dmzlink-bw
neighbor 10.0.7.38 dmzlink-bw
neighbor 10.0.7.46 dmzlink-bw
After you’ve enabled the DMZ Link Bandwidth feature, you have to clear the EBGP sessions with the clear ip bgp address soft in command. As before, you can check the load balancing behavior with the show ip bgp prefix and show ip route prefix commands.
PE-A#show ip bgp 10.2.2.0
BGP routing table entry for 10.2.2.0/24, version 7
Paths: (2 available, best #2, table default)
Multipath: eBGP iBGP
Flag: 0x1820
Advertised to update-groups:
1
65001
10.0.7.46 from 10.0.7.46 (10.0.1.5)
Origin IGP, metric 0, localpref 100, valid, external, multipath
DMZ-Link Bw 500 kbytes
65001
10.0.7.38 from 10.0.7.38 (10.0.1.5)
Origin IGP, metric 0, localpref 100, valid, external, multipath, best
DMZ-Link Bw 125 kbytes
PE-A#show ip route 10.2.2.0
Routing entry for 10.2.2.0/24
Known via "bgp 65000", distance 20, metric 0
Tag 65001, type external
Last update from 10.0.7.38 00:00:43 ago
Routing Descriptor Blocks:
* 10.0.7.46, from 10.0.7.46, 00:00:43 ago
Route metric is 0, traffic share count is 240
AS Hops 1
Route tag 65001
10.0.7.38, from 10.0.7.38, 00:00:43 ago
Route metric is 0, traffic share count is 59
AS Hops 1
Route tag 65001
