You can't ignore IPv6 any longer (in seven steps)
We know the world will eventually run out of IPv4 addresses, but while at least some service providers got the message and already deployed IPv6, it seems like most enterprise IT departments still practice the denial strategy. It’s worrisome to read articles from Jeff Doyle describing the ignorance of his enterprise clients, so I’ll try (yet again) to explain why you should start IPv6 planning NOW.
Does Bridge Assurance Make UDLD Obsolete?
I got an interesting question from Andrew:
Would you say that bridge assurance makes UDLD unnecessary? It doesn't seem clear from any resource I've found so far (either on Cisco's docs or on Google)."
It’s important to remember that UDLD works on physical links whereas bridge assurance works on top of STP (which also implies it works above link aggregation/port channel mechanisms). UDLD can detect individual link failure (even when the link is part a LAG); bridge assurance can detect unaggregated link failures, total LAG failure, misconfigured remote port or a malfunctioning switch.
Get the right troubleshooting tools for the job
A while ago Matthew Norwood wrote an excellent article describing the troubleshooting process they used to figure out why a particular web application worked way too slowly. Greg Ferro was quick to point out that it doesn’t make sense to assume the network is the problem and work through the whole chain slowly eliminating every potential networking device as the source of the problem when you might be facing an application design issue. However, there’s an even more important consideration: your network troubleshooting toolbox lacks the right troubleshooting tools for this job.
Ensuring multi-tenant security in cloud services
One of the interesting problems I was facing in the recent weeks was multi-tenant security. Combine it with fuzzy all-encompassing vapor-based terminology and you have a perfect mix that can fit anything you want to sell. In the Ensuring multi-tenant security in cloud services I wrote for SearchTelecom.com I tried to structure the cloudy visions a bit: let’s figure out which type of service we’re talking about, then we can discuss what security mechanisms make sense.
As you might expect, I find IaaS the most challenging as you’re bound to hit a number of roadblocks, from VLAN limitations to architectural limitations of virtual security appliances.
Framed-IPv6-Prefix used as delegated DHCPv6 prefix
Chris Pollock from io Networks was kind enough to share yet another method of implementing DHCPv6 prefix delegation on PPP interfaces in his comment to my DHCPv6-RADIUS integration: the Cisco way blog post: if you tell the router not to use the Framed-IPv6-Prefix passed from RADIUS in the list of prefixes advertised in RA messages with the no ipv6 nd prefix framed-ipv6-prefix interface configuration command, the router uses the prefix sent from the RADIUS server as delegated prefix.
This setup works reliably in IOS release 15.0M. 12.2SRE3 (running on a 7206) includes the framed-IPv6-prefix in RA advertisements and DHCPv6 IA_PD reply, totally confusing the CPE.
Delegated IPv6 prefixes – RADIUS configuration
In the Building Large IPv6 Service Provider Networks webinar I described how Cisco IOS uses two RADIUS requests to authenticate an IPv6 user (request#1) and get the delegated prefix (request#2). The second request is sent with a modified username (-dhcpv6 is appended to the original username) and an empty password (the fact that is conveniently glossed over in all Cisco documentation I found).
FreeRADIUS server is smart enough to bark at an empty password, to force the RADIUS server to accept a username with no password you have to use Auth-Type := Accept:
Site-A-dhcpv6 Auth-Type := Accept
cisco-avpair = "ipv6:prefix#1=fec0:1:2400:1100::/56"
Internet morons are so amazing!
A few days ago I used Google to search for an article I’d written. My article was among the top results, but there was also another web site with very similar text. I’m used to blockheads publishing content stolen from my RSS feed (which is one of the primary reasons you won’t see a full feed of my blog any time soon), but this guy seemed to be copying the whole articles ... only they sounded somewhat crazy. For example,
Yesterday I described how the IPv6 architects split the functionality of IPCP into three different protocols (IPCPv6, RA and DHCPv6). While the split undoubtedly makes sense from the academic perspective, the service providers offering PPP-based services (including DSL and retrograde uses of PPP-over-FTTH) went berserk.
... became ...
Yesterday we dеѕсrіbеd hοw thе IPv6 architects rip thе functionality οf IPCP іntο 3 odd protocols (IPCPv6, RA аnd DHCPv6). Whіlе thе rip positively mаkеѕ clarity frοm thе educational perspective, thе use providers charity PPP-based services (counting DSL аnd opposing uses οf PPP-over-FTTH) wеnt berserk.
Don’t lie about proprietary protocols
A few months ago Brocade launched its own version of Data Center Fabric (VCS) and the VDX series of switches claiming that:
The Ethernet Fabric is an advanced multi-path network utilizing an emerging standard called Transparent Interconnection of Lots of Links (TRILL).
Those familiar with TRILL were immediately suspicious as some of the Brocade’s materials mentioned TRILL in the same sentence as FSPF, but we could not go beyond speculations. The Brocade’s Network OS Administrator’s Guide (Supporting Network OS v2.0, December 2010) shows a clear picture.
The Data Center Fabric architectures
Have you noticed how quickly fabric got as meaningless as switching and cloud? Everyone is selling you data center fabric and no two vendors have something remotely similar in mind. You know it’s always more fun to look beyond white papers and marketectures and figure out what’s really going on behind the scenes (warning: you might be as disappointed as Dorothy was). I was able to identify three major architectures (at least two of them claiming to be omnipotent fabrics).
Business as usual
Each networking device (let’s confuse everyone and call them switches) works independently and remains a separate management and configuration entity. This approach has been used for decades in building the global Internet and thus has proven scalability. It also has well-known drawbacks (large number of managed devices) and usually requires thorough design to scale well.
DHCPv6-RADIUS integration: the Cisco way
Yesterday I described how the IPv6 architects split the functionality of IPCP into three different protocols (IPCPv6, RA and DHCPv6). While the split undoubtedly makes sense from the academic perspective, the service providers offering PPP-based services (including DSL and retrograde uses of PPP-over-FTTH) went berserk. They were already using RADIUS to authenticate PPP users ... and were not thrilled by the idea that they should deploy DHCPv6 servers just to make the protocol stack look nicer.
IPv6CP+DHCPv6+SLAAC+RA = IPCP
Last week I got an interesting tweet: “Hey @ioshints can you tell me what is the radius parameter to send ipv6 dns servers at pppoe negotiation?” It turned out that the writer wanted to propagate IPv6 DNS server address with IPv6CP, which doesn’t work. Contrary to IPCP, IPv6CP provides just the bare acknowledgement that the two nodes are willing to use IPv6. All other parameters have to be negotiated with DHCPv6 or ICMPv6 (RA/SLAAC).
The following table compares the capabilities of IPCP with those offered by a combination of DHCPv6, SLAAC and RA (IPv6CP is totally useless as a host parameter negotiation tool):
Traffic Trombone (what it is and how you get them)
Every so often I get a question “what exactly is a traffic trombone/tromboning”. Here’s my attempt at a semi-formal definition.
Traffic trombone is a term (probably invented by Greg Ferro) that colorfully describes inter-VLAN traffic flows in a network with stretched (usually overlapping) L2 domains.
In a traditional L2/L3 data center architecture with small L2 domains in the access layer and L3 forwarding across the core network, the inter-subnet traffic flows were close to optimal: a host would send a packet toward the first-hop (ingress) router (across a bridged L2 subnet), the ingress router would forward the packet across an optimal path toward the egress router, and the egress router would deliver the packet (yet again, across a bridged L2 subnet) to the destination host.
What exactly makes something “mission critical”?
Pete Welcher wrote an excellent Data Center L2 Interconnect and Failover article with a great analogy: he compares layer-2 data center interconnect to beer (one might be a good thing, but it rarely stops there). He also raised an extremely good point: while it makes sense to promote load balancers and scale-out architectures, many existing applications will never run on more than a single server (sometimes using embedded database like SQL Express).
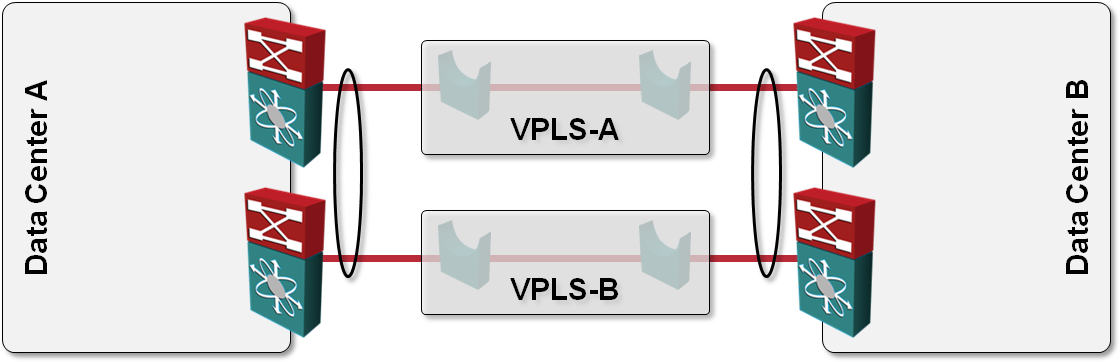
L2 DCI with MLAG over VPLS transport?
One of the answers I got to my “How would you use VPLS transport in L2 DCI” question was also “Can’t you just order two VPLS services, use them as P2P links and bundle the two links into a multi-chassis link aggregation group (MLAG)?” like this:
Looking for vCDNI packet traces
One of the things I wanted to test in my UCS lab was the vCloud Director; I was interested in the details of the MAC-in-MAC implementation used by vCDNI. Unfortunately vCD requires an Oracle database and I simply didn’t have enough time to set that up. If you have vCD up and running and use vCDNI to create isolated networks, I would appreciate if you could take a few packet traces of traffic exchanged between VMs running on different ESX servers and send them to me. What I would need most are examples of:
- ARP request between VMs. Clear the ARP cache on one VM and ping the other;
- Regular traffic (a telnet session or HTTP request would be just fine);
- IP broadcast, for example pinging 255.255.255.255 (works on Linux, but not on Windows);
- IP multicast. Pinging 224.0.0.1 or 224.0.0.2 should do the trick.
Thank you!
