netlab VLAN Trunk Example
Last week I described how easy it is to use access VLANs in netlab. Next step: VLAN trunks.
We’ll add two Linux hosts to the lab topology used in the previous blog post, resulting in two switches, two Linux hosts in red VLAN and two Linux hosts in blue VLAN.
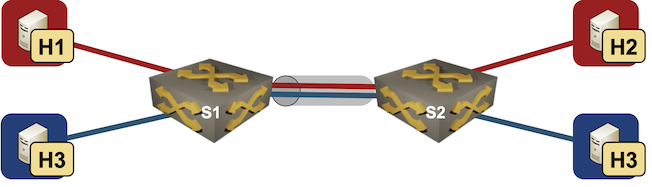
Lab topology
Like in the previous example, we’ll use groups in the lab topology file to define our devices. Members of the hosts group will be Linux containers, members of the switches group will be Arista EOS containers using vlan configuration module:
provider: clab
nodes: [ h1, h2, h3, h4, s1, s2 ]
groups:
hosts:
members: [ h1, h2, h3, h4 ]
device: linux
switches:
members: [ s1, s2 ]
module: [ vlan ]
device: eos
Next, we’ll define the VLANs. We need red and blue VLANs; as before, netlab will assign 802.1q tags to VLANs as needed.
vlans:
red:
blue:
Finally, we need links between nodes. Access VLANs with be defined on switch interfaces. List of VLANs in the VLAN trunk will be defined on the link itself, as it applies to all nodes connected to the trunk. Note that we’re working with VLAN names and don’t have to worry about the VLAN 802.1q tags.
links:
- h1:
s1:
vlan.access: red
- h3:
s1:
vlan.access: blue
- s1:
s2:
vlan.trunk: [ red, blue ]
- h2:
s2:
vlan.access: red
- h4:
s2:
vlan.access: blue
And that’s all you have to do. Execute netlab up1 and enjoy your first multi-VLAN lab.
Here are the relevant parts of Arista cEOS configuration (for the two readers who still don’t have a working netlab environment):
spanning-tree mode mstp
!
vlan 1000
name red
!
vlan 1001
name blue
!
interface Ethernet1
mac-address 52:dc:ca:fe:05:01
switchport access vlan 1000
!
interface Ethernet2
mac-address 52:dc:ca:fe:05:02
switchport access vlan 1001
!
interface Ethernet3
description s1 -> s2
mac-address 52:dc:ca:fe:05:03
switchport trunk allowed vlan 1000-1001
switchport mode trunk
!
interface Vlan1000
description VLAN red (1000) -> [h1,s2,h2]
ip address 172.16.0.5/24
!
interface Vlan1001
description VLAN blue (1001) -> [h3,s2,h4]
ip address 172.16.1.5/24
Want to run this lab on your own, or try it out with different devices? No problem:
- Install netlab
- Download the relevant containers or create Vagrant boxes
- Download the topology file into an empty directory
- Execute netlab up
- Enjoy! 😊
-
After doing the mandatory homework like creating a Ubuntu VM, installing the software, and downloading Arista cEOS container. ↩︎
