Blog Posts in August 2007
DHCP conflict logging: the true story
The on-line configuration help for the ip dhcp conflict logging configuration command (logging: Record address conflicts in a log file) is one of the more misleading texts I've found in Cisco IOS (and the CCO documentation is not much better). Here's how it actually works ...
Track interface IP routing detects incorrect interface state
MPLS LDP Autoconfiguration
Most MPLS books (mine included) and courses tell you that you have to manually enable MPLS on each interface where you want to run it with the mpls ip interface configuration command. However, this task was significantly simplified in IOS release 12.3(14)T with the introduction of MPLS LDP autoconfiguration. If you use OSPF as the routing protocol in your network, you can use the mpls autoconfig ldp [area number] router configuration command to enable LDP on all interfaces running OSPF (optionally limited to an OSPF area).
As the careful readers of my MPLS books know, it’s dangerous to run LDP with your customers; the moment you run LDP with them (Carrier’s carrier model is an exception), they can insert any labeled packet into your network, bypassing inbound access lists and sending traffic where it’s not supposed to go (even into another VPN). It’s vital that you consider security implications before deploying MPLS LDP autoconfiguration.
Using this feature on P routers is absolutely safe, as they have no customer links. You have to be more careful on the PE routers, more so if you run routing protocols with your customers. The safest configuration method would be to configure LDP autoconfiguration inside a single OSPF area, but even then, a configuration error (placing a PE-CE interface in a wrong area) could open your network to MPLS-based attacks.
Insert Responses to Command Prompts in Tclsh
I have been aware of the typeahead Tcl command for months, but somehow I never got it to work.
It works perfectly in IOS release 12.4(15)T; this is what you have to do to clear interface counters:
Skip the “show ip route” legend
Install a Static Route When an IP Address Is NOT Reachable
One of my readers recently asked an interesting question: “How do you install a static route when an IP address is not reachable?”
Without going into the design reasons that prompted the question, you can actually track when IP SLA measurement fails with an obscure configuration syntax of the track objects that tracks when another track object fails.
Warm reload does not change the config register
DHCP-based static routes
ip route 10.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 dhcpYou could use this functionality in scenarios where your core network uses DHCP (for example, in metropolitan networks using layer-2 Ethernet transport from an ISP), but your router needs a different default route.
You can also use this feature to change the administrative distance of the DHCP-based default route (or you could use the ip dhcp-client default-router distance value configuration command that one of the readers described in a comment to a previous DHCP-related post).
Any other good ideas where this might come handy? Post them as comments ...
Reload a Router from Tcl Script
event manager applet forceReloadNow you can use the exec "event manager run forceReload" Tcl command in your Tcl script to run the applet (and reload the router).
event none
action 1.0 reload
Notes:
- To execute file management commands from Tcl shell, you have to disable prompts with file prompt quiet configuration command;
- This article is part of You've asked for it series.
Import DHCP options from an upstream DHCP server
If your router gets its IP address from an upstream DHCP server, it can automatically import the other DHCP options (DNS server, WINS server, domain prefix etc.) into its DHCP pools. For example, if you use a router to connect to a cable or MAN Ethernet ISP (see the following figure), you can use the DHCP option import to minimize your router configuration (and make it fail safe from any changes in the ISP network).
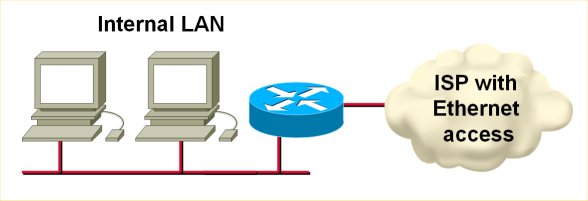
To configure the DHCP option import, use the import all DHCP pool configuration command. You cannot select which options you want to import, but you can override them with other DHCP pool configuration commands.
OSPF Graceful Shutdown
Reloading a core router in a high-availability network is always a tricky proposition. Even if you tweak the routing protocol hello timers (or use fast L2 mechanisms to detect next-hop loss), it still takes a few seconds for the routing protocols to converge. For example, when using OSPF, the adjacent routers have to detect the neighbor loss, change their router LSAs, flood them (LSA flooding is rate-limited), the changed LSAs have to be propagated across the whole area and all routers in the area have to run SPF (which is also rate-limited).
It would be much better if you could gracefully take a router offline by increasing the OSPF cost on all its interfaces, thus forcing an OSPF SPF run while the router is still capable of forwarding the traffic (resulting in no packet loss).
Default DHCP client-id
Obviously, if your ISP checks your MAC address (and at least most cable operators do), you might have a problem. To make the router behave like a workstation, use the ip address dhcp client-id interface-name configuration command. The new client ID will be the MAC address of the specified interface (which can be different from the interface you're configuring).
Example: Tcl script with command-line parameters
In a comment to the “Execute multiple commands at once” post, Michal has asked for a complete Tcl-shell-with-parameter example. Here's a short script that shuts down the interface and displays its status:
- Variable ifname is set to the value of the first command-line parameter (in many other programming languages, this would be written as argv[0]);
- If the ifname is empty, the script aborts and prints the usage guidelines (again, in a more human-oriented programming language, this would be if (ifname == “”) ...);
- The show ip interface ifname command is executed. If it fails, the interface name is not correct and the script aborts.
- IOS configuration commands interface ifname and shutdown are executed.
- The show ip interface brief configuration command is executed and filtered with the interface name.
#
# ifname is set to first CLI parameter (interface name)
#
set ifname [lindex $argv 0]
if {[string equal $ifname ""]} { puts "Usage: shutdown ifname"; return; }
if { [ catch { exec "show ip interface $ifname" } errmsg ] } {
puts "Invalid interface $ifname, show ip interface failed"; return}
ios_config "interface $ifname" "shutdown"
puts [ exec "show ip interface brief ¦ include $ifname" ]
If you store this Tcl script into your flash as shutdown.tcl and configure alias exec shutdown tclsh flash:shutdown.tcl, you can execute the command shutdown Serial0 to shut down the serial interface.
Notes:
- The last show command will display the interface status only if the specified interface name exactly matches the actual IOS interface name (whereas the rest of the script accepts shortcut names). The more generic matching algorithm is left as an exercise for the reader
- For more in-depth information on Tclsh implementation on Cisco IOS, read the IOS Tclsh resources.
- This article is part of You've asked for it series.
Re-enable debugging without EEM
Notes:
- The router expects a newline character at the end of the configuration file. The best way to ensure it's always there is to add a comment line at the end of the file
- The configuration file load usually fails immediately after the reboot, as the interfaces and IP routing processes are not yet fully operational. You might thus miss the first few seconds of the router's operations (unless you store the extra configuration file Flash or NVRAM).
Sample configuration: periodic upload of router configuration
Pete Vickers sent me a very interesting configuration sample:
To get an IOS device to upload it’s configuration periodically to an external FTP server:
ip ftp source-interface loopback 0
ip ftp username ftp_username
ip ftp password ftp_password
file prompt quiet
!
kron policy-list backup
cli copy running-config ftp://10.20.30.40
!
kron occurrence daily-backup at 0:30 recurring
policy-list backup
The beauty of this example is that you can use it on platforms that don't support Embedded Event Manager (which has a very similar cron functionality) as the kron commands were introduced in 12.2T and 12.3 IOS releases.
Note: You have to use the file prompt quiet configuration command as the commands executed by kron cannot supply any user input
Conditional OSPF Default Route: Tested Configuration
One of my readers asked for a working configuration of the conditional OSPF default route advertisement feature. In my scenario, the OSPF default route would be announced whenever an Internet prefix (172.18.0.0/16) would be present in the IP routing table.
