Tight Control over Route Leaking
Articles » Tight Control over Route Leaking
The introduction of EIGRP route leaking on the stub routers has to be based on a thoroughly checked network design. Imagine a scenario where the link bandwidth between A2 and B2 is significantly lower than the one between A1 and B1:
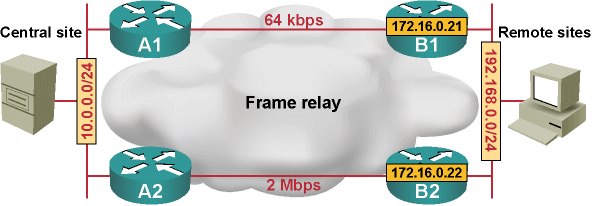
Remote site with a primary and a backup uplink
If the route leaking is configured on B1 and B2 to leak the default route, B2 will leak the default route back to A2, which will store it in its EIGRP topology database:
a2#show ip eigrp topology 0.0.0.0
IP-EIGRP (AS 1): Topology entry for 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0
State is Passive, Query origin flag is 1, 1 Successor(s), FD is 28160
Routing Descriptor Blocks:
0.0.0.0 (Null0), from 0.0.0.0, Send flag is 0x0
Composite metric is (28160/0), Route is Internal
Vector metric:
Minimum bandwidth is 100000 Kbit
Total delay is 100 microseconds
Reliability is 255/255
Load is 1/255
Minimum MTU is 1500
Hop count is 0
Exterior flag is set
172.16.1.6 (Serial0/0/0.101), from 172.16.1.6, Send flag is 0x0
Composite metric is (41029120/2174976), Route is Internal
Vector metric:
Minimum bandwidth is 64 Kbit
Total delay is 40200 microseconds
Reliability is 255/255
Load is 1/255
Minimum MTU is 1500
Hop count is 3
Exterior flag is set
Due to limitations on querying the stub routers (DUAL queries are never sent to these routers), the leaked routes could persist in the EIGRP topology tables even after the original IP prefix (on which they were based) is no longer reachable, resulting in temporary routing loops.
EIGRP routers eventually arrive to the correct final routing topology even when stub routers nondiscriminatory leak core routes. However, the convergence time is increased as is the chance of introducing temporary loops (which never occur when using the regular DUAL algorithm).
To alleviate the possibility of a routing loop in EIGRP networks with stub routers leaking routes to their neighbors, the route leaking has to be tightly controlled – you have to match a combination of IP prefixes and the outgoing interface in the route-map attached to the EIGRP stub router with the leak-map keyword. In our sample network, the route map would thus perform the following route selection:
- Default route (0.0.0.0/0) would only be leaked to the LAN interface;
- Stub router loopback addresses would only be leaked to the WAN interface (uplink to the central site).
This setup prevents the default route from being leaked back to the core routers. It also prevents the loopback addresses from the remote site from being readvertised back into the same remote site. The relevant parts of the router configuration are included in the next printout:
router eigrp 1
network 0.0.0.0
no auto-summary
eigrp stub connected leak-map TightEigrpLeak
!
ip access-list standard EigrpDefault
permit 0.0.0.0
ip access-list standard EigrpLoopback
permit 172.16.0.16 0.0.0.15
!
route-map TightEigrpLeak permit 100
match ip address EigrpDefault
match interface FastEthernet0/0
!
route-map TightEigrpLeak permit 200
match ip address EigrpLoopback
match interface Serial0/0/0.100
With the corrected route-map, the default route is no longer advertised from B2 to A2, while the loopback address of B1 is advertised to A2 from A1 (as it receives the IP prefix from B1) and B2 (which leaks the IP prefix received from B1):
a2#show ip eigrp topology 0.0.0.0
IP-EIGRP (AS 1): Topology entry for 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0
State is Passive, Query origin flag is 1, 1 Successor(s), FD is 28160
Routing Descriptor Blocks:
0.0.0.0 (Null0), from 0.0.0.0, Send flag is 0x0
Composite metric is (28160/0), Route is Internal
Vector metric:
Minimum bandwidth is 100000 Kbit
Total delay is 100 microseconds
Reliability is 255/255
Load is 1/255
Minimum MTU is 1500
Hop count is 0
Exterior flag is set
a2#show ip eigrp topology 172.16.0.21 255.255.255.255
IP-EIGRP (AS 1): Topology entry for 172.16.0.21 255.255.255.255
State is Passive, Query origin flag is 1, 1 Successor(s), FD is 2300416
Routing Descriptor Blocks:
10.0.0.5 (FastEthernet0/0), from 10.0.0.5, Send flag is 0x0
Composite metric is (2300416/2297856), Route is Internal
Vector metric:
Minimum bandwidth is 1544 Kbit
Total delay is 25100 microseconds
Reliability is 255/255
Load is 1/255
Minimum MTU is 1500
Hop count is 2
172.16.1.6 (Serial0/0/0.101), from 172.16.1.6, Send flag is 0x0
Composite metric is (40642560/156160), Route is Internal
Vector metric:
Minimum bandwidth is 64 Kbit
Total delay is 25100 microseconds
Reliability is 255/255
Load is 1/255
Minimum MTU is 1500
Hop count is 2
